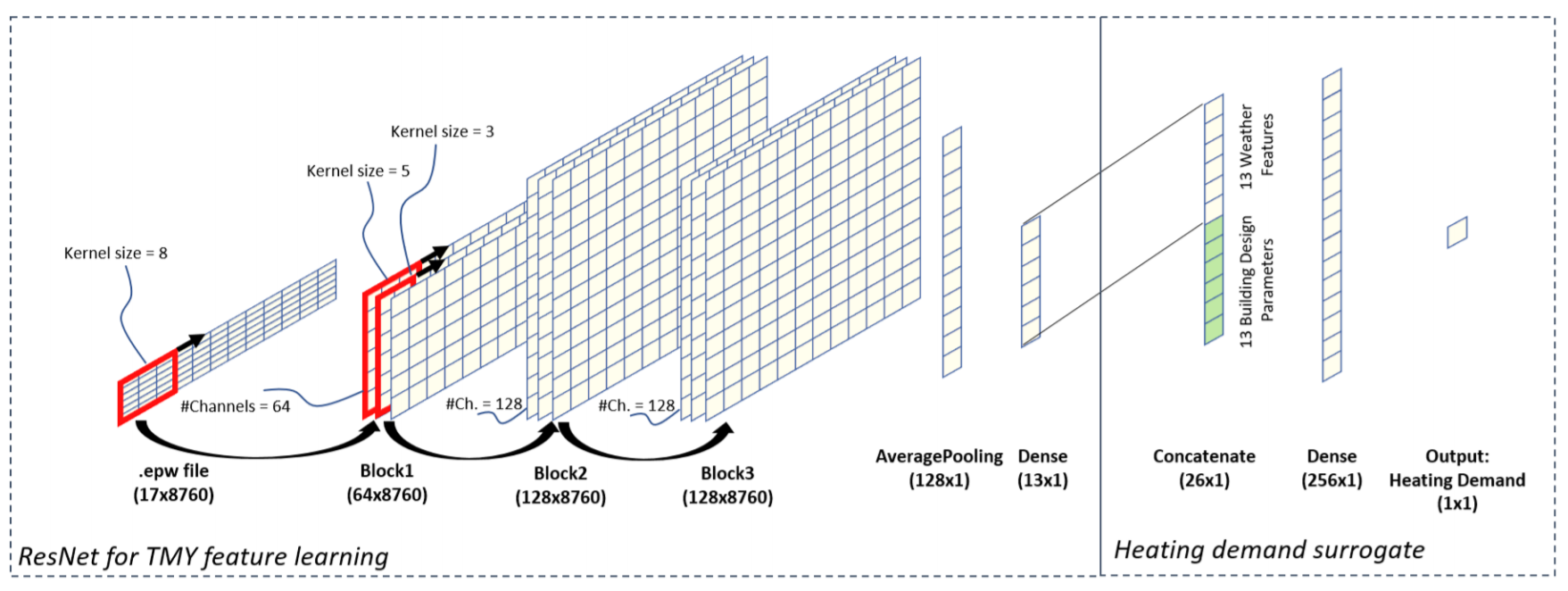
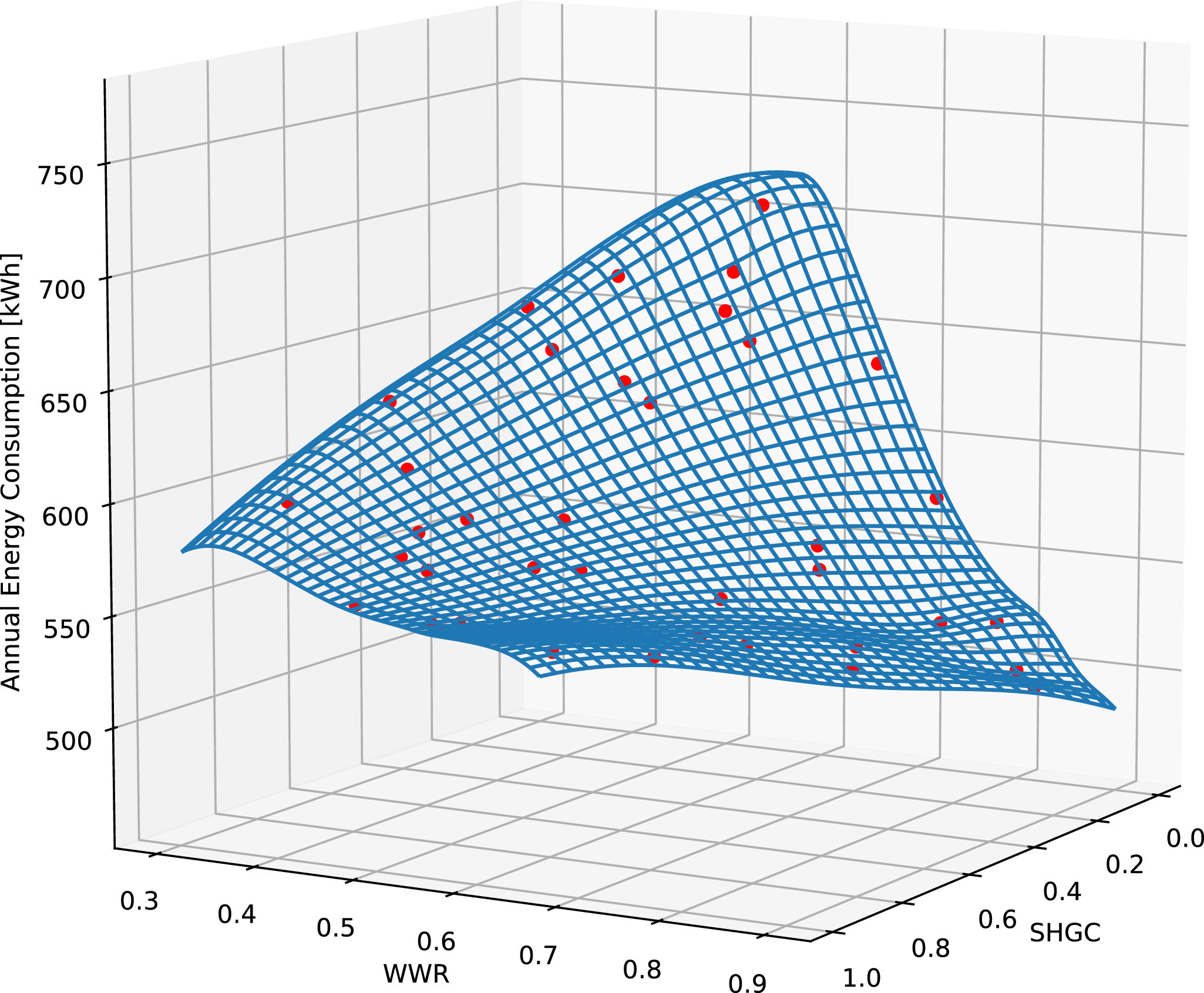
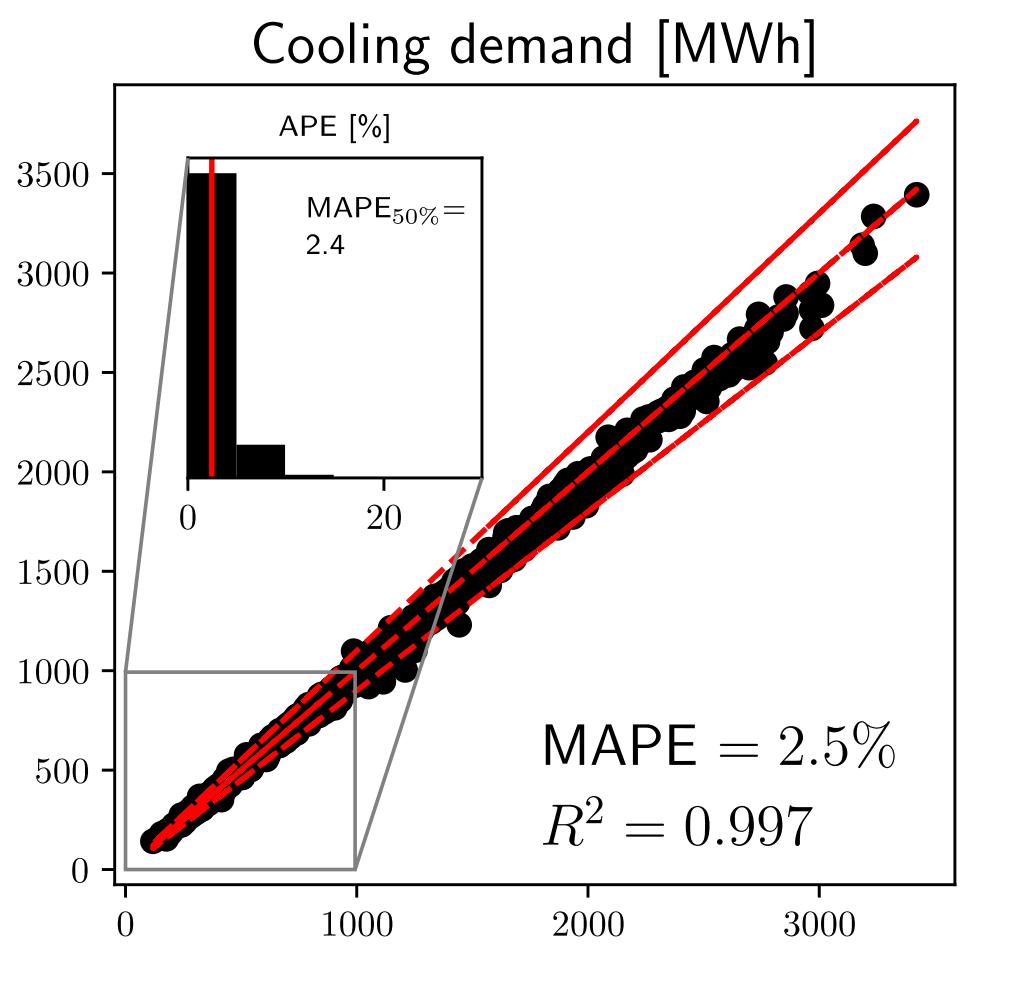
API
Use these endpoints to access Building Energy Ninja programmatically.
Fast Prediction
Endpoint: /fast/prediction Method: GET
Returns a CSV file with hourly heating or cooling loads.
Required query parameters
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|
weather | Weather file identifier | AFG_FYB_Maymana.AP.409220_TMYx.2004-2018.epw |
bt | Building type | commercial or residential |
load | Load type | heating or cooling |
Building design parameters (13)
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|
cna | North Axis [degrees] | 123 |
cuv | U-value [W/(mK)] | 0.05 |
cwit | Wall insulation thickness [m] | 0.12 |
cwt | Window transmittance | 0.201 |
cwc | Window conductivity [W/(mK)] | 0.042 |
cwsa | Wall solar absorptance | 0.8 |
chs | Heating setpoint [°C] | 19.25 |
ccs | Cooling setpoint [°C] | 25.98 |
ceg | Equipment Gains [W/m²] | 12 |
clg | Light Gains [W/m²] | 10 |
cvr | Ventilation rate [m³/(s·Person)] | 0.0067 |
cir | Infiltration rate [m³/(s·m²)] | 0.0001 |
cwwr | Window-to-wall ratio | 0.87 |
Examples
cURL
curl -O "http://localhost:5000/fast/prediction?weather=AFG_FYB_Maymana.AP.409220_TMYx.2004-2018.epw&bt=residential&cna=123&cuv=0.05&cwit=0.12&cwt=0.201&cwc=0.042&cwsa=0.8&chs=19.25&ccs=25.98&ceg=12&clg=10&cvr=0.0067&cir=0.0001&cwwr=0.87&load=heating"
Python (requests)
import requests
url = "http://localhost:5000/fast/prediction"
params = {
"weather": "AFG_FYB_Maymana.AP.409220_TMYx.2004-2018.epw",
"bt": "residential",
"cna": 123,
"cuv": 0.05,
"cwit": 0.12,
"cwt": 0.201,
"cwc": 0.042,
"cwsa": 0.8,
"chs": 19.25,
"ccs": 25.98,
"ceg": 12,
"clg": 10,
"cvr": 0.0067,
"cir": 0.0001,
"cwwr": 0.87,
"load": "heating"
}
response = requests.get(url, params=params)
with open("energy_loads.csv", "wb") as f:
f.write(response.content)
Node.js
const https = require('https');
const fs = require('fs');
const params = new URLSearchParams({
weather: 'AFG_FYB_Maymana.AP.409220_TMYx.2004-2018.epw',
bt: 'residential',
cna: 123,
cuv: 0.05,
cwit: 0.12,
cwt: 0.201,
cwc: 0.042,
cwsa: 0.8,
chs: 19.25,
ccs: 25.98,
ceg: 12,
clg: 10,
cvr: 0.0067,
cir: 0.0001,
cwwr: 0.87,
load: 'heating'
});
const url = `http://localhost:5000/fast/prediction?${params.toString()}`;
https.get(url, (response) => {
const file = fs.createWriteStream('energy_loads.csv');
response.pipe(file);
});
Response
- Index: Hourly timestamps starting from 1/1/2020 (8760 hours)
- Column: Energy load values in kWh (column header is the weather file name)
- Filename: CSV download
Additional Endpoints
/weather/list
Parameters: search (optional), format (json | csv)
curl "http://localhost:5000/weather/list?format=json"
Example JSON:
{
"total": 7305,
"weather_files": [
{
"filename": "AFG_FYB_Maymana.AP.409220_TMYx.2004-2018.epw",
"city": "Maymana",
"altitude": 824.0,
"hdd": 4523.0,
"coordinates": [67.5, 35.93]
}
]
}
/weather/download
Parameter: id (e.g., AFG_FYB_Maymana)
curl -O "http://localhost:5000/weather/download?id=AFG_FYB_Maymana"
Finding Weather Files
- Use
/weather/list to search.
- Or run
list_weather_files.py locally:
python list_weather_files.py --search "CAN"
python list_weather_files.py --json
python list_weather_files.py --csv
- Weather metadata lives at
src/static/sourcedata.geojson.